Pain in the knee joint is a very common phenomenon in a person's life. It can be due to many factors. As a rule, the main reason is that due to its anatomical structure, the knee joint is quite vulnerable to injury, it is subjected to huge daily loads, especially in overweight people. It is also possible for a symptom to appear during intense sports activities, in the course of daily household or professional activities.
Causes of knee pain

The knee joint consists of many different elements, each of which carries its own functional load. Why do my knees hurt? The following factors can cause pain in the knee joint:
- traumatization;
- damage;
- dystrophy of any of the elements.
Pain in the knees is a symptomatic manifestation of a huge number of diseases of the knee joint. What causes knee pain? To accurately determine the cause in a specific case, diagnostic measures are necessary. Pain can be the result of trauma to the elements:
- ligament apparatus;
- tendon formations;
- damage to the cartilage shell.
For various diseases of the knee, in addition to pain, specific manifestations determined in laboratory, instrumental and other tests will be characteristic.
Arthritis
If the knees hurt after a long period of rest or heavy loads, this is arthritis. This pathology of the knee joint is found in about 5-15% of patients who consult a doctor for pain in the joint area.
Fact! Arthritis is a disease characteristic of all age groups of the population, but young people are more susceptible to the disease.
A characteristic sign of most arthritis is acute pain in the knee, i. e. acute onset - within 1-2 days.
Arthritis is an inflammatory process, so acute pain in the knee joint is accompanied by such signs:
- swelling;
- swelling;
- hyperemia;
- severe pain that worsens at night.
In arthrosis and damage to the cartilage of the meniscus, pain occurs or increases with motor load on the knee joint, i. e. the pain will be relieved if there is no load on the knee, unlike arthritis. In arthritis, the pain syndrome has a different etiology, and it will not work to get rid of it by reducing the load and immobilizing the joint. In addition, arthritis can affect several joints at once, except for the knee.
arthrosis
Another very common disease of the knee accompanied by severe pain. Pathology is found in 35-40% of people who come with knee pain, as a rule, this age category is over 40 years old, both the left knee and the right knee are often affected at the same time. Severe pain may not appear immediately, but the sensations gradually increase over time: for someone a week or two, for someone - for a month. Unlike arthritis, the knee only hurts when you put weight on it:
- Initially, a person feels pain after a long walk.
- Over time, even walking short distances brings a lot of discomfort.
- Later, the patient has great difficulty going up and down stairs.
- It is difficult to get up from a chair, that is, unfold your knees with a load.
- The pain syndrome disappears if you rest, immobilize the joint.
Over time, without proper treatment, the symptoms worsen significantly:
- the joint is deformed;
- there is a creaking sound when walking or extending the knee.
- the pain intensifies.
The pathogenesis is due to the destruction of the structure, degeneration of the cartilage lining of the joint cavity, which leads to deformation of the joint. Primary arthrosis or age-related arthrosis occurs as a result of the natural wear and tear of cartilage, secondary - is the result of injuries or a number of other reasons. Such causes can be infectious arthritis, tumor lesions of bone or cartilage tissue, as a result of which this disease can appear in people of different age categories.
Meniscopathies
They are also a common cause of joint pain.
For reference! Among patients who sought help due to pain in the knee joint, about 25-35% have meniscus injuries of various etiology.
This pathology is observed in people of any age, different professional activities and is equally common in men and women. Menisci are injured during active movements:
- At the time of injury, a characteristic click is heard, after which the knee may suddenly hurt.
- Then a crunch or crepitus in the knee.
- Then a sharp pain is felt, which intensifies.
- A person in this condition cannot move at all in the knee joint.
The pain may subside after some time and the meniscopathy becomes chronic. But without proper treatment, edema develops, the joint swells and movements in it can be blocked, which is accompanied by severe pain and can lead to the development of arthrosis. The risk group is:
- people suffering from gout or arthritis of the joints;
- diabetics;
- people with weak ligaments or overweight.
The disease is diagnosed with the help of computed tomography or nuclear magnetic resonance and is treated, depending on the severity, conservatively or surgically.
Tendinitis
Tendinitis is an inflammatory process in the tissues of the tendons of the muscle, at the place of their attachment. This disease most often affects active children and adolescents, athletes:
- cyclists;
- basketball players;
- volleyball players;
- athletes.
The disease exists in two forms:
- Tenosynovitis is an inflammation of the tendon sheath.
- Tendobursitis is a lesion of the tendon bag.
The cause of this phenomenon can be not only an injury related to active movement, but also such diseases:
- gout;
- arthritis;
- immunodeficiency conditions;
- infectious diseases;
- excessive physical activity;
- muscle imbalance of the forces acting on the joint.
In tendinitis, the knees hurt paroxysmally, i. e. the pain increases with loading of the tendon, in severe forms or in the later stages of the disease, rupture of the inflamed tendon is possible. The disease is diagnosed in different ways, sometimes it can be detected by laboratory methods, for example, when the cause is an infection.
But if the cause is gout or inflammatory processes in the joint itself, then the methods of X-ray examination and nuclear magnetic resonance can detect the disease.
In the initial stages of development of the disease, conservative therapy helps, which includes immobilizing the joint with plaster and limiting motor activity. Different drugs are prescribed:
- tissue repair agents;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antibiotics.
Physiotherapy procedures are also prescribed. In advanced cases, with necrosis, surgical removal of dead tissue and plastic tendon formations is performed.
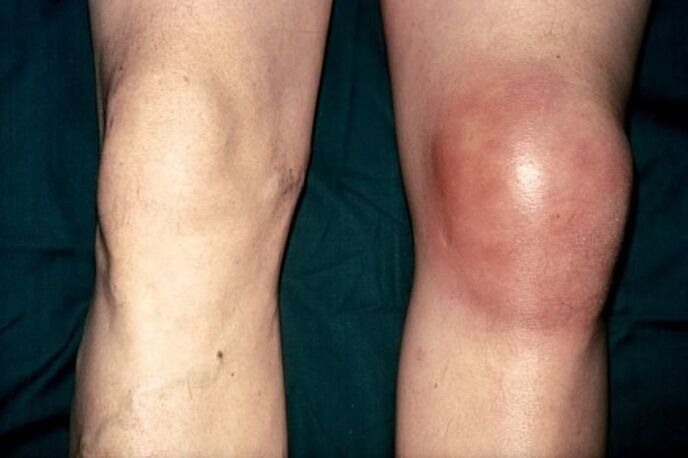
knee bursitis
It is a disease of the joint bags, characterized by an inflammatory process and the presence of exudative fluid.
For reference! The causes of bursitis are constant, excessive load on the joint.
If we are talking about pathologies of an infectious nature, then the following factors can be the cause:
- skin damage in the knee area;
- open wound injuries;
- various septic conditions;
- the presence of an infection in the blood;
- Overweight;
- increased load on the joint.
Also, the pathology is secondary, as a complication of gouty disease or arthritis of the knee joint. Like any inflammatory process, bursitis will be accompanied by symptoms:
- pain syndrome;
- noticeable changes in the shape of the joint;
- the presence of swelling in the knee area;
- redness;
- severely impaired movement.
The severity and visibility of these manifestations will depend on the severity and localization of the process.
Depending on the localization of the inflamed joint capsule, there are the following types of pathology:
- prepatellar;
- co-parent;
- infrapatellar bursitis.
This pathology, as a rule, is quite easily diagnosed and treated, except for cases with elderly patients, where it is chronic and difficult to treat.
Baker's cyst
Another pathological phenomenon of the knee joint, which brings with it a lot of pain and trouble. The cyst is also called a popliteal hernia, it is a bulge in the popliteal fossa. Usually, between the tendons, gastrocnemius and semimembranosus muscles on the back surface of the knee region, there is an intertendinous bag. As a result of the following factors, a pathological effusion is formed in the joint cavity, which penetrates into the intertendon bag:
- trauma;
- dystrophic changes;
- inflammatory processes.
As a result, the bag enlarges, becomes noticeable, and this is called a Baker's cyst. In the initial stages of development, it can be invisible, not cause obvious discomfort, that is, be asymptomatic. Later, due to the increase in size, the knee hurts a lot, because the cyst begins to press on the nerves and blood vessels, and the mobility of the joint is also impaired. Flexion movements become difficult and are also accompanied by severe pain.
Dissecting osteochondrosis
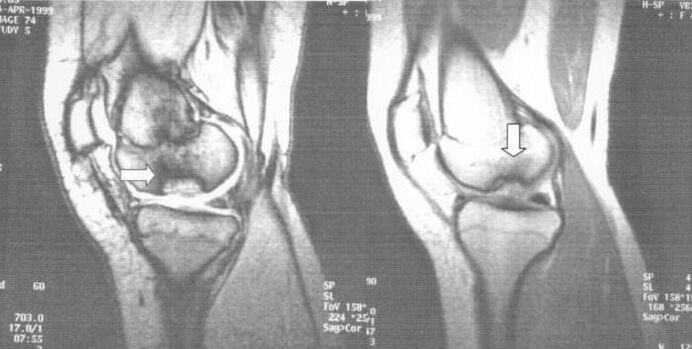
This disease is also a common cause of knee pain. Normally, the articular surfaces that make up the knee joint are lined with cartilage. This pathology is due to the fact that a small part of the cartilage shell necrotizes and exfoliates, as a result of which a loose body is formed in the joint cavity, which causes many problems.
It manifests symptomatically as follows:
- mild pain and discomfort;
- when moving, the pain intensifies;
- swelling may develop.
A separate fragment of cartilage tissue, once in the joint cavity, can interfere with the movement of which patients complain, and when moving, you can hear characteristic clicks or crunches. After exfoliation of the smooth joint surface, a defect remains, which contributes to traumatizing the joint and will lead to osteoarthritis or other pathologies in the future.
Doctors believe that frequent trauma to the joints is the reason for the development of this disease, but sometimes there are patients who have no previous injuries. The diagnosis is based on the methods of computed tomography, nuclear magnetic resonance and X-ray examination.
Gout disease
Gout or gouty arthritis of the knee joint occurs as a result of impaired metabolism, which leads to excessive formation and deposition of uric acid salts, the so-called urates. They accumulate both in the joint cavity itself and around the cartilage and tendons and cause inflammation.
With the disease, there is severe pain in the joint, the knee area becomes red and swollen. If gout becomes chronic, then the urate deposits cause a clear deformity of the joint, resulting in impairment, an inability to perform a normal range of motion.
The disease is diagnosed using X-rays and blood tests for uric acid. It is difficult to treat, but in the initial stages of development, special diets and drug treatment are used.
The causes of knee pain can be many different pathologies with completely different etiology and pathogenesis. So only a specialist doctor can answer with certainty the question of why the knee hurts after the diagnosis.
General principles of treatment
Everyone wonders what to do if the knee hurts? Many people, with the appearance of slight pain, discomfort, prefer to endure, because they think that it will pass by itself, this should not be done. The knee joint hurts because it is a manifestation of various pathologies, and in the absence of timely adequate therapy, these pathologies can lead to serious consequences.
If the knees hurt, then the treatment includes the therapy of the pathology that caused the pain. Based on the results of the diagnostic tests, the doctor prescribes appropriate therapy and decides how to treat the diseased joints. These can be the following methods:
- special therapeutic and preventive exercises;
- ointments;
- compresses.
In case of inflammatory phenomena, anti-inflammatory substances are prescribed, and if there are problems with cartilage tissue, various chondroprotectors or corticosteroid drugs.
For reference! It is possible to perform a puncture, both for diagnosis and for treatment, for example in the case of Becker's cyst.
Sometimes, with advanced pathology, surgical treatment is indicated, which is also diverse. In most cases, they resort to arthroscopic operations: to remove the joint body or resection of the area of the affected tissue. Also, if other therapy is ineffective, knee arthroplasty is used, that is, replacement of joint elements or the entire joint with an artificial implant. Thus, the answer to the question "what to do if the knee hurts" is an immediate visit to the doctor.













































